By Tim Bochnowski
The foot / pedal connection is one of the most valuable aspects of any bike fit because our experience shows us that a lot of a rider’s pain and discomfort can originate in the feet. Proper pedal setup can help eliminate foot and knee pain as well as help you increase your power on the bike. Todays’ pedal systems have greatly improved and shoes have gotten stiffer. Clipless pedals are easy to enter and exit and offer a variety of adjustments. Adjusting pedals and cleats is extremely important. Here’s how…
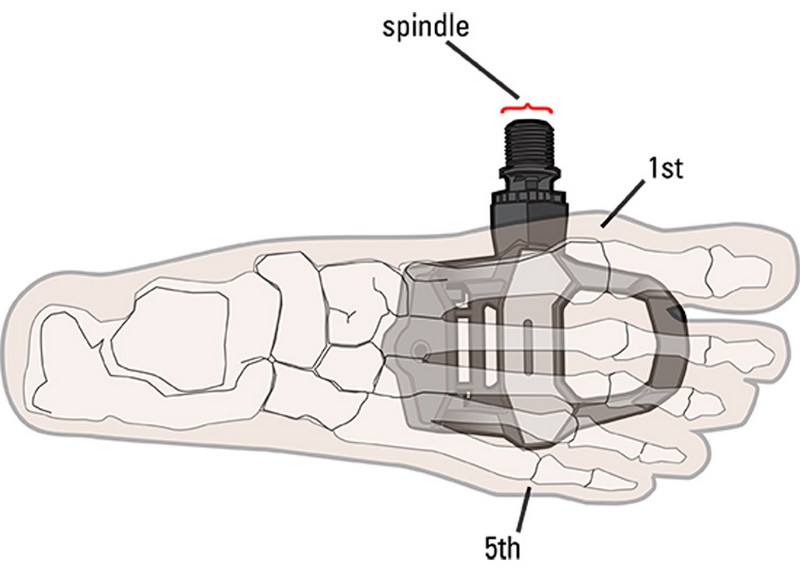 First, adjust fore/aft cleat position. Generally, the ball of your foot should be directly over the pedal axle. While some cyclists find positioning the center of their cleat behind the ball of their foot (the bump on the inside of your foot behind the big toe) comfortable, others like to place the center of the pedal spindle even closer to the bump (behind the pinky toe) on the outside of the foot. If you feel strain in your calf, have toe numbness or burning pain in the ball of the foot, try moving your cleat slightly rearward on your shoe. If you feel sore under the arch, try moving your cleat slightly forward. Also, making sure you are not over tightening your shoe straps and your toes are not jammed into the end of your shoes will aid in comfort.
First, adjust fore/aft cleat position. Generally, the ball of your foot should be directly over the pedal axle. While some cyclists find positioning the center of their cleat behind the ball of their foot (the bump on the inside of your foot behind the big toe) comfortable, others like to place the center of the pedal spindle even closer to the bump (behind the pinky toe) on the outside of the foot. If you feel strain in your calf, have toe numbness or burning pain in the ball of the foot, try moving your cleat slightly rearward on your shoe. If you feel sore under the arch, try moving your cleat slightly forward. Also, making sure you are not over tightening your shoe straps and your toes are not jammed into the end of your shoes will aid in comfort.
Second, check side-to-side cleat position, also clinically called medial/lateral cleat placement. Medial means toward the inside and lateral means toward the outside. One of the best ways to determine side-to-side cleat position is to look at knee over toe alignment. Generally, the foot should be below the knee when pedaling. If the knee is over the outside of the foot, move the foot outward by pushing the cleat inward on the shoe. If the knee goes inward toward the bicycle frame when you pedal, then the foot may need to be moved inward (cleat moved toward the outside of the shoe) to be more under the knee. Not all cleats or shoes allow for side-to-side adjustment. Some pedal systems offer different length spindles, or you can increase stance width (also sometimes referenced as Q-factor) by adding spacer washers to the pedal axles.
Third, forefoot tilt and angle is very important and often overlooked. Foot “hot spots”, inward knee dives and leg length issues could be addressed by insoles, wedging and shimming. BIKEFIT® Cleat Wedges® inventor Paul Swift states that over 90% of the population’s feet tilt inward or outward. If interested in having your forefoot or leg length checked, contact a bicycle fitting professional trained in wedging.
Finally, cleat rotation needs to be addressed. In general, the direction your feet point off the bike will be the same as when you are on the bike. When you walk, do your feet point outward or inward? If you jumped into the air, after landing, are your feet pointing straight ahead? The goal is to get your feet to automatically be in the center of the cleat’s rotational arc. Most cleats allow between 3-9 degrees of rotational float. Adjust the cleat so you’re centered and not constantly pressing up against the return spring or cleat release. Make sure when adjusting your cleats that your anklebones don’t hit the crank or your heels hit the chain stays of the bicycle.
A proper fit on your bicycle will result in increased comfort, more power, and better handling. Try the tips given above at home. To fine-tune your foot/pedal position, and your overall fit on your bike, schedule an appointment with a well-trained and experienced fitter. Comfort breeds performance. Keep working at improving your position on your bike.
Tim Bochnowski is a bicycle fitter and owner of Mountain Velo LLC (mountainvelo.com), a cycling performance center located in Park City, UT. Tim started fitting bicycles in 1985 and has been trained by BIKEFIT, Slowtwitch, Retul and several other fitting techniques and tools.












[…] Kemudian juga yang penting adalah menyesuaikan posisi cleat di pedal dengan posisi kaki, yang bagus katanya posisinya seperti gambar di bawah ini yaitu di antara ruas tulang jempol dan jari manis di kaki, di referensi […]
Comments are closed.